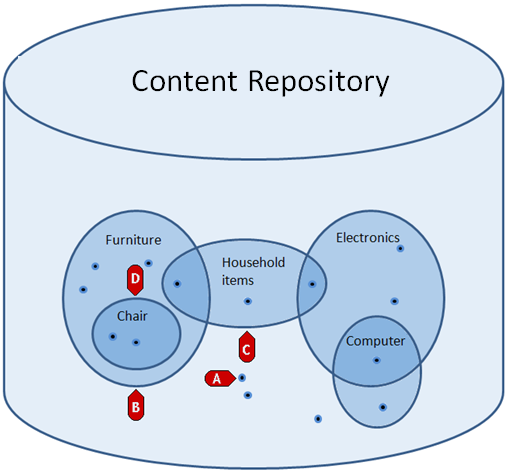
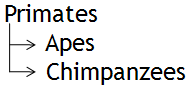In the XperienCentral"s Content Repository, you can assign keywords (terms) to objects. By assigning one or more terms to an object, you can control when and how these objects are retrieved and displayed on your web site. In addition to assigning one or more terms to an object, you can create thesaurus relationships between terms in order to fine-tune the results returned by the Media Overview content element. Creating relationships between terms forms the basis of a thesaurus, which in its strictest sense is defined as "a categorized index of terms for use in information retrieval". Consider the following:
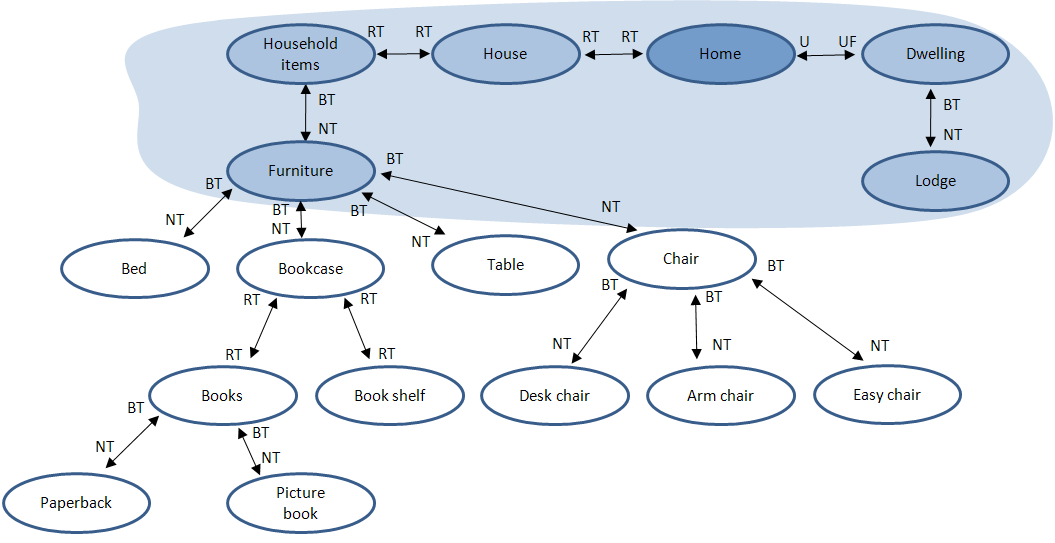
In the figure above, objects in the Content Repository are represented by the small circles. The shaded ovals represent keyword terms (Furniture, Electronics, and so forth). The objects within the shaded ovals have that keyword or keywords assigned to them. The relationship between various objects/terms are as follows:
- An item with no keyword (term) assigned to it (A).
- A term assigned to six different Content Repository items (B).
- An item with one term assigned to it and related to two others through a thesaurus relationship (C).
- Two items with four terms related to them through a thesaurus relationship (D).
When you specify a term in a Media Overview element, the objects that are returned are directly affected by the thesaurus relationships between that term (the source term) and the terms it has a thesaurus relation with. From the example above, if you specify the term "Household items", three objects will be returned. If you specify "Computer", two objects will be returned, and so forth.
In This Topic
Term Relationships
Thesaurus relationships between keyword terms are broken down into the following three categories:
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
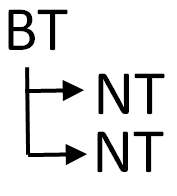
Hierarchical | Hierarchical relationships are used to define broader and narrower scopes between terms. A broader term is a wider generalization of a narrower term, for example "vehicle" can be used to describe a "truck", "car", "motorcycle" and "bicycle". In this example, "vehicle" is the broader term and "truck", "car", "motorcycle" and "bicycle" are narrow terms for "vehicle". Likewise, "compact", "sub-compact" and "sedan" are narrower terms for the broader term "car". A broader/narrower term relationship can also be referred to as a parent/child relationship. Child terms sharing the same parent are referred to as siblings. In XperienCentral, when you define a term as being a broader or narrow term for another, the reciprocal relationship is automatically created. For example if you assign "vehicle" as the broader term for "car", "car" is automatically assigned as a narrower term for "vehicle". In thesaurus nomenclature, broader terms are abbreviated as "BT" and narrower terms are abbreviated as "NT", for example:
|
| Equivalency | Equivalency relationships are used primarily to tie synonyms and near-synonyms together. Oftentimes the equivalency relationship acts as a bridge or tie between an official or preferred term and one or more unofficial or casual versions. For example the "United States of America" is the official name of the country but it is also commonly referred to as "The US" and "America". In XperienCentral's thesaurus nomenclature, equivalency relationships are tied together using "Use for" (U) and "Is used for" (UF) indicators. "Use for" and "Is used for" terms always have a reciprocal relationship, for example if "The United of America" has an "Is used for" relationship with "America" then "America" automatically has a "Use for" relationship with "The United States of America". |
| Associative | Associative relationships are used in cases where the relationship between the terms is neither of the above types. For example, "Information technology" is related to "computers" in the sense that information technology is managed and made possible by computers but the relationship is neither hierarchical nor equivalent. In XperienCentral's thesaurus nomenclature, associative relationships are referred to using the "related to" (RT) indicator. |
Broader/Narrower Term Relationships
Broader and narrower term relationships are used to establish parent/child relationships between terms in a hierarchy. For example, in the following simple hierarchy containing three terms, "Primates" is the broader term (parent) of "Apes" and "Chimpanzees":
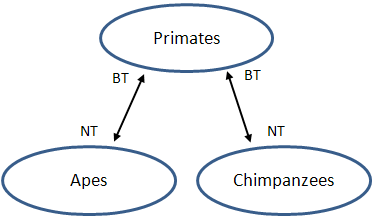
You use broader/narrower terms to create term hierarchies. In this example, "Primates" is defined as a broader term for "Apes" and "Chimpanzees" and conversely, "Apes" and "Chimpanzees" as narrower terms for "Primates". Symbolically the relationship can be conveyed as in the figure below where the abbreviation "BT" stands for broader term and "NT" for narrower term:
When you add a broader or narrower term relationship, the reciprocal relationship is also created at the same time. For example, adding "Apes" as a narrower term for "Primates" also adds "Primates" as a broader term for "Apes".
Use for/Is Used for Relationships
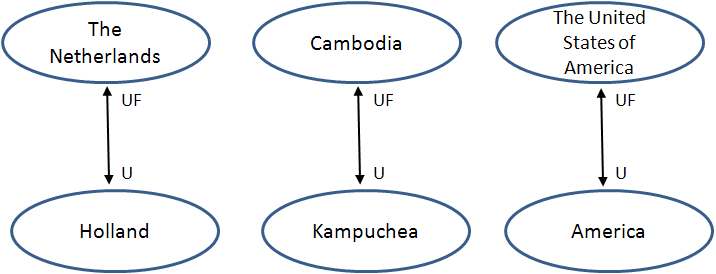
Use for/Is used for term relationships allow you to create a relationship between two or more terms that denote the same thing when one of them is the more common or preferred term for the entity in question. "Is used for" and "Use for" terms are always reciprocal. This relationship is used in a variety of situations, such as when you want to tie terms together with synonyms or near synonyms of the term. Consider the following place names:
- Holland/The Netherlands
- Kampuchea/Cambodia
- America/The United States of America
The first name listed in each line does identify the country in question, but it is less precise than the second name listed. For historical reasons, the country "The Netherlands" has been also identified by the name of "Holland" and it is a meaningful substitute, however it is not the preferred term. In such cases it is useful to create a "Use for/Is used for" relationship between these two names in order to ensure that any reference to "Holland" also points to objects identified with the preferred term "The Netherlands". In the example below, the "Use for/Is used for" relationships between terms can be conveyed as follows. In the figure, "UF" stands for "Is used for" and "U" stands for "Use for":
Thus, any term that references or that have a thesaurus relationship with "Holland" will also lead to terms that have a thesaurus relationship with "The Netherlands".
The meaning of "User for" and "Is used for" in the context of the current term can be a little confusing. When a term has a "Use for" term assigned to it, you should read the relationship as "Use for the current term the term X". For example, if the term "America" has a "Use for" relationship with the term "The United States of America", read it as "Use for America the term The United States of America". When a term has an "Is used for" term assigned to it, you should read the relationship as "The 'Is used for' term is used for the current term". Thus, if the term "America" has an "Is used for" relationship with the term "The United States of America", read it as "The United States of America is used for America".
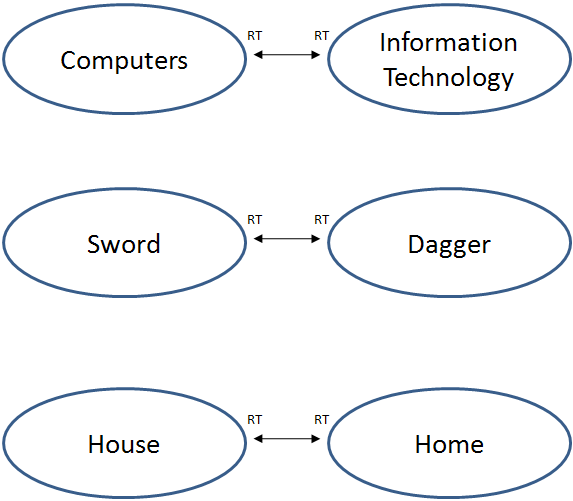
Related Term Relationships
Related term relationships (RT) are used primarily for terms that have neither a hierarchical nor equivalent relationship. Related terms have an associative relationship and bear a close conceptual relationship with the main term. You can also think of the "RT" relationship as a "See also" reference.
For example:
Term Depth
How terms are related to each other in the thesaurus has a direct effect on the number of objects that are retrieved from the Content Repository when a term is referenced in a Content Overview or Dynamic Content Overview content element. This is because for each thesaurus relationship that a term has, it automatically has relationships with other terms through their defined relationships. For each thesaurus relation type in XperienCentral, rules are applied to determine what the wider context of thesaurus relations is as a result of the stepping that is performed from one term to another. The stepping between relationships determines what a term's wider thesaurus context is. For each thesaurus relationship type, a predefined number steps between terms is followed from a source term. The number of steps (term depth) that is followed for each thesaurus term relationship in XperienCentral is:
| Relationship | Depth |
|---|---|
| Broader term (BT) | 1 step |
| Narrower term (NT) | 3 steps |
| Related to (RT) | 2 steps |
| Use for (U) | 1 step |
| Is used for (UF) | 1 step |
The implications of the stepping rules are described for each of the thesaurus relationships below.
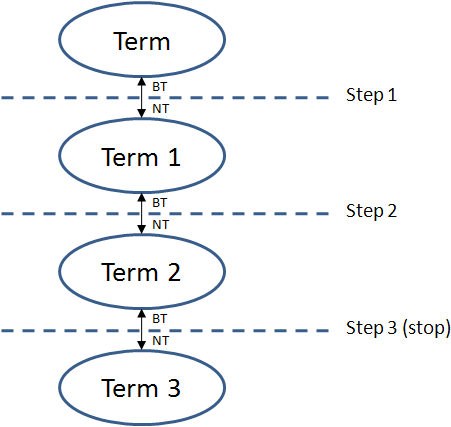
Narrower Term Relationship
From a source term, XperienCentral will follow a chain of three steps through successive NT relationships and then stop. In the following example, if the source term is "Term", it will have a thesaurus relationship with "Term 1", "Term 2", and "Term 3". The relation between "Term" and "Term 1" is a direct relationship, that is, they are tied directly together through a "Broader/Narrower term" (BT/NT) relationship. The relationship between "Term" and "Term 2" and "Term" and "Term 3" is indirect, as is that between "Term1" and "Term 3":
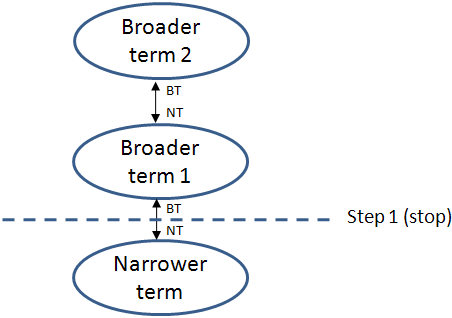
Broader Term Relationship
From a source term, XperienCentral will step to a broader term and stop. A step from a narrower term to a broader can only happen in the context of a direct relationship between the two. From the stepped-to term (the broader term), no other broader terms will be stepped to. For example, if "Narrower term" is the source term, "Broader term 1" is considered a relation but "Broader term 2" is not:
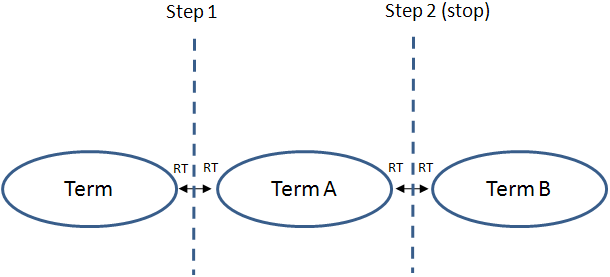
Related to
For terms that are related to each other, XperienCentral will follow a chain of two successive "related to" steps to other terms from the source term and then stop. In the following example, if "Term" is the source term, it has a direct relationship with "Term A" and an indirect relationship with "Term B":
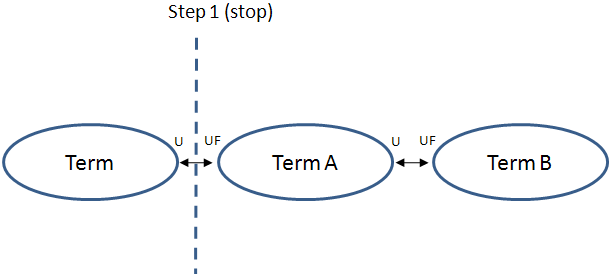
Use for/Is used for
For "Use for" and "Is used for" relationships, XperienCentral will step from the source term to the "Use for" or from the source to the "Is used for" term and then stop. A term must have the relationship "Use for" or "Is used for" directly with the source term, that is, it cannot be reached through an indirect relationship. Once a "Use for" or "Is used for" step is completed, no further "Use for" or "Is used for" relations can be made. In the example below, "Term" has a direct relationship with "Term A" but not with "Term B" and vice versa.
Multiple Relationship Depths
The examples above describe simple situations where all the relationships are the same, for example from a broader term to a narrower term that is itself a broader term for a subsequent narrower term ,and so forth, to a depth of three (BT > NT > NT > NT). In reality, thesaurus relations consist of complicated combinations of relationship types (BT/NT, U/UF, and RT). How terms are related to each other through combinations of the relationship types has a direct effect on the outcome of the broader context thesaurus relationships a term has. This section describes how the stepping process in complex thesaurus relationships works.
The overall number of steps that XperienCentral will follow from a source term to the other terms it is tied to through thesaurus relationships is 3. This means that the depth rule for each of the relationship types is affected by the number of steps that precede it as well as the type of relationship that results in a term being stepped to. The table below describes how each successive step affects the depth to which each of the thesaurus relationship types is followed.
| Relationship | Steps available from source | Depth after 1 step | Depth after 2 steps | Depth after 3 steps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broader term (BT) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Narrower term (NT) | 3 | 2 or 0 (When a source term steps to a broader term, the number of available NT steps for the broader term becomes 0 because a broader/narrower term pairing is a parent/child relationship. This prevents the siblings of the child (narrower/source) term from being selected because they are not logically related.) | 1 | 0 |
| Related to (RT) | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Use for (U) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Is used for (UF) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
For example, given the rules set forth in the table above, if you step from a source term to a term tied to it through a "related to" relation (RT) and that term has three levels of narrower terms under it, XperienCentral will only step to two of the three levels of narrower terms. This is because the NT depth rule after step 1 is 2.
In order to illustrate the depth rules, the following six examples are given in order to show how thesaurus relationships and depth rules determine which terms will be determined to have a broader context relationship with a source term and thus which content items will be returned by a Content Overview or Dynamic Content overview content element containing the source term(s).
In the examples below, the following symbols/acronyms are used:
Term Depth Example 1
| Terms related to source term | Description |
|---|---|
| Home | Source term. Available steps from Home: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Dwelling | 1 UF step from Home. Available steps from Dwelling: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Lodge | 1 UF step from Home. Available steps from Lodge: UF/U = 0 RT = 0 BT = 0 |
| House | One RT step from Home. Available steps from House UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Household items | 1 RT step from House. Available steps from Household items: UF/U = 0 RT = 0 BT = 0 NT =1 |
| Furniture | 1 NT step from Household items. Available steps from Furniture: None. |
Term Depth Example 2
| Terms related to source term | Description |
|---|---|
| House | Source term. Available steps from House: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Home, Household items | 1 RT step from House. Available steps from Home and Household items: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Furniture | 1 NT step from House. Available steps from Furniture: UF/U = 0 RT = 0 BT = 0 NT =1 |
| Bed, Bookcase, Table, Chair | 1 NT step from Furniture. Available steps from Bed, Bookcase, Table, and Chair: None. |
Term depth example 3
| Terms related to source term | Description |
|---|---|
| Bookcase | Source term. Available steps from Bookcase: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Furniture | 1 BT step from Bookcase. Available steps from Furniture: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 0 Note: The number of NT steps for Furniture becomes 0 because the sibling terms Bed, Table, and Chair are not logically related to Bookcase. |
| Books, Book shelf | 1 1 RT step from Bookcase. Available steps from Book shelf: UF/U = 0 RT = 0 BT = 0 NT =1 |
| Paperback, picture book | 1 NT step from Books. Available steps from Paperback and Picture book: None. |
Term depth example 4
| Terms related to source term | Description |
|---|---|
| Table | Source term. Available steps from Table: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Furniture | 1 BT step from Table. Available steps from Furniture: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 0 Note: The number of NT steps for Furniture becomes 0 because the sibling terms Bed, Bookcase, and Chair are not logically related to Table. |
Term depth example 5
| Terms related to source term | Description |
|---|---|
| Books | Source term. Available steps from Books: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Bookcase | 1 RT step from Books. Available steps from Bookcase: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Book shelf | 1 1 RT step from Bookcase. Available steps from Book shelf: UF/U = 0 RT = 0 BT = 0 NT = 1 Note: There is one NT depth left to step, however, since Book shelf has no NT relations, stepping stops |
| Paperback, picture book | 1 NT step from Books. Available steps from Paperback and Picture book : UF/U = 0 RT = 0 BT = 0 NT = 2 Note: There are two NT depths left to step, however, since these two terms have no NT relations, stepping stops. |
Term depth example 6
| Terms related to source term | Description |
|---|---|
| Home | Source term. Available steps from Home: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Dwelling | 1 UF/U step from Home. Available steps from Dwelling: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Lodge | 1 NT step from Dwelling. Available steps from Lodger: UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 1 |
| House | 1 RT step from Home. Available steps from House : UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Household items | 1 RT step from House. Available steps from Household items : UF/U = 0 : RT = 0 : BT = 0 : NT =1 : |
| Furniture | Source term. Available steps from Furniture: UF/U = 1 RT = 2 BT = 1 NT = 3 |
| Bed, Bookcase, Table, Chair | 1 NT step from Furniture. Available steps from Bed, Bookcase, Table, and Chair : UF/U = 0 RT = 1 BT = 0 NT = 2 |
| Books, book shelf | 1 RT step from Bookcase. Available steps from Books and Book shelf : UF/U = 0 : RT = 0 : BT = 0 : NT = 1 |
| Paperback, Picture book | 1 NT step from Books. Available steps from Paperback and Picture book : None |
Content Repository Article Example
This section provides a practical example of how thesaurus relationships affect how articles are returned by a Media Overview element. The following articles have been added to the Content Repository and they have the following terms assigned to them:
| Article | Assigned terms |
|---|---|
| New clue to the cause of muscular dystrophy uncovered | Science |
| Hubble telescope repairs delayed | Science |
| iPhone 5 now available | Technology |
| YouTube announces mobile device support | Technology |
| Coen brothers win best picture honors | Movies |
| David Geffen leaves DreamWorks | Movies |
| US entertainment considers tightening ratings | Entertainment |
| London Philharmonic hires new music director | Music |
| Beckham signs with AC Milan | Sports |
| Benelux countries hope to host 2018 World Cup | Sports |
The following thesaurus relationships have been created between the following terms:
| Term | RT | BT | NT | UF | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Science | Technology | ||||
| Technology | Science | Tech | |||
| Movies | Entertainment | ||||
| Entertainment | Movies, Music, Sports | ||||
| Music | Entertainment | ||||
| Sports | Entertainment | ||||
| Tech | Technology |
Article example 1
Based on the table above, the following articles are shown when a Media Overview element is placed on a page based on the keyword "Tech":
- YouTube announces mobile device support
- iPhone 5 now available
- New clue to the cause of muscular dystrophy uncovered
- Hubble telescope repairs delayed
Article Example 2
Based on the table above, the following articles are shown when a Media Overview element is placed on a page based on the keyword "Entertainment":
- Benelux countries hope to host 2018 World Cup
- Beckham signs with AC Milan
- London Philharmonic signs new music director
- US entertainment industry considers tightening ratings
- Coen Brothers win best picture Oscar
- David Geffen leaves DreamWorks